
With over 23 billion text messages sent per day, SMS is certainly one of the most popular communication tools. Whether it’s a friendly text for a dear one or a piece of business-critical information, the ‘power of 160 characters’ has refined the way we express ourselves. What’s more fascinating is the fact that no matter when, where, and what these text messages are about, they reach their true destination, every single time. But who ensures this seamless transmission? Let me introduce you to SMSC – Short Message Service Center, an intermediary between mobile devices, that ensures reliable transmission of SMS messages between senders and recipients. It plays a pivotal role in the handling of SMS messages and delivers a seamless SMS communication service.
Throughout this post, I will explain the various aspects associated with SMSCs. So let’s get started!
What is a Short Message Service Center (SMSC)?
SMSC Meaning: An SMSC i.e. Short Message Service Center is an intermediary unit in the mobile telephone network that handles SMS-related operations. It is responsible for storing, forwarding, converting, and delivering SMS messages. In other words, we can say that an SMSC performs the job of routing SMS messages between senders and recipients. This means that whenever a text message is sent, it is first received by the SMSC which then forwards it to the intended recipient.
Insight: An SMSC is also called an SMS Center, Message Center, Text Message Center, etc.
In case the recipient device is unavailable, the SMSC temporarily stores the message for a certain period and forwards it when the recipient becomes available. There are certain scenarios when SMSCs temporarily store text messages in a dedicated space. The most common instances are:
- When the recipient’s device is switched off, SMSC stores the message for a specific time
- When message traffic is at peak, then SMSC stores the message and queues until ready for delivery
- Messages that are scheduled such as campaigns are stored by SMSCs and released at the specified time
Once the SMSC finds that the recipient’s device is available again, it will resend the message. After the defined period, the message gets deleted and will no longer be available for dispatch to the recipient even if their device is available.
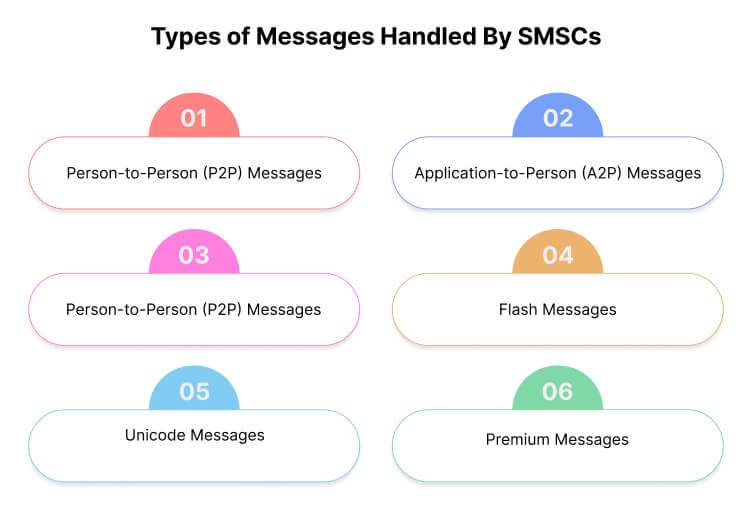
What Types of Messages Are Handled By SMSCs?
SMSCs primarily handle text messages composed of up to 160 characters. These messages can include various types of content such as:
-
Person-to-Person (P2P) Messages
We all are familiar with traditional text messages such as greetings sent between individuals using their mobile phones such as friends, family members, and colleagues.
-
Application-to-Person (A2P) Messages
These messages originate from applications, services, or businesses and are sent to individual users. A2P communication usually involves transactional alerts such as account balance notifications and one-time passwords, order confirmations, and promotional messages like special discounts and offers.
-
Person-to-Application (P2A) Messages
P2A communication involves users sending text messages to applications or services. Some common examples are users subscribing to services, participating in contests via voting, etc.
-
Flash Messages
Such messages appear directly on the mobile device’s screen even if the device is locked. Flash messages are usually used for conveying critical information such as emergency alerts, special events, service disruptions, etc. SMSCs employ special protocols to ensure the delivery of flash messages.
-
Unicode Messages
Text messages that include characters beyond the basic 7-bit alphabet are unicode messages i.e. usage of emoticons, special characters, etc. SMSCs handle the conversion and encoding of Unicode characters for proper delivery.
-
Premium Messages
Also called Premium Rate SMS, these SMS messages are incurred at a higher cost to the sender than the standard SMS. SMSCs manage the billing and routing of Premium SMS messages between the sender, recipient, and content provider.
Looking at the types of messages handled by the SMSCs, we can say that SMSCs demonstrate significant versatility. In the next section, we shall learn about SMSC number
What is an SMSC Number?
Also called an SMSC Address or Message Center Number, an SMSC number is a number that identifies an SMSC on a network. It is in the format of a standard phone number and is used by your MNO i.e. Mobile Network Operator to route and deliver SMS messages. The SMSC address is stored on the user’s SIM card and, each MNO has a unique SMSC address for their subscribers.
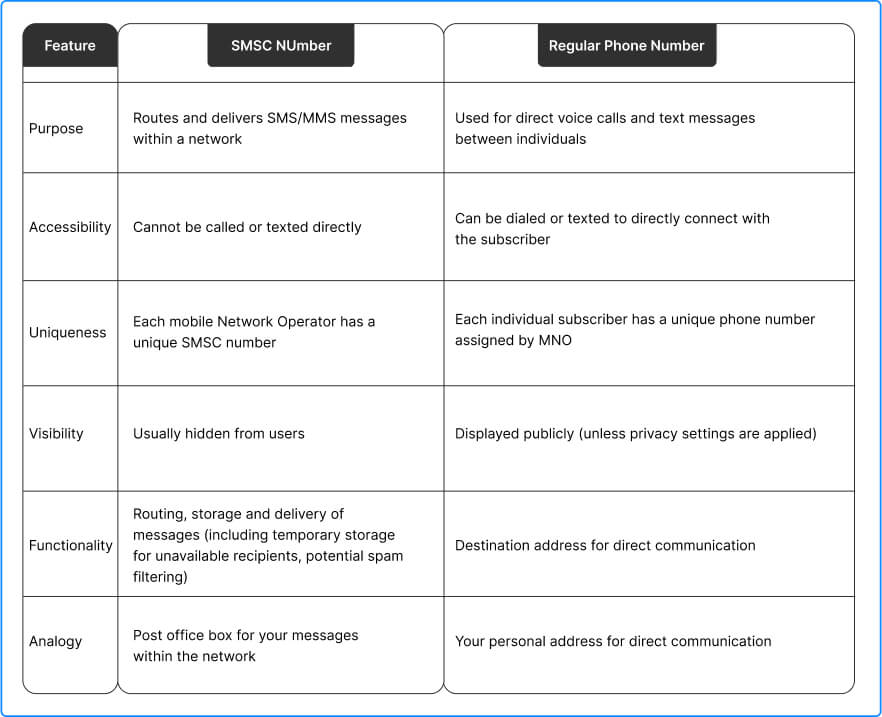
How is an SMSC Number Different from a Phone Number?
It is important to learn that an SMSC number is different from a regular phone number as it cannot be called or texted directly. Usually, users don’t need to manually set the SMSC number as it comes pre-configured. However, in some cases, manual configuration might be required.
SMSC Number vs. Regular Phone Number
SMSC Number on Android and iOS
If you need to check or update the SMSC number on your Android and iOS devices, then here’s how you can do it.
How to Set the Message Center Number in Android?
Method 1: Using Messaging App Settings
- Open the Messaging app you use for sending and receiving SMS/MMS messages.
- Tap the Menu button (usually three dots) or swipe right from the left edge of the screen.
- Select Settings.
- Look for options like Advanced, SMS, or Message Center.
- Tap on the option mentioned in the above step.
- You should see a field labeled Message Center Number or SMSC Number.
- Enter the correct message center number for your mobile network operator (MNO). You can find this number on your operator’s website or by contacting their customer service.
- Save the changes by tapping OK or Save.
Method 2: Using Phone App (for older Android versions)

- Open the Phone app on your device.
- Tap the Menu button or swipe right from the left edge of the screen.
- Select Settings.
- Look for options like Call settings or More settings.
- Tap on the option mentioned in step 4.
- Look for an option named SMS Center or Message Center.
- Tap on it and enter the correct message center number for your MNO.
- Save the changes by tapping OK or Save.
How to Set the Message Center Number in Apple iOS?

On iOS devices, you can directly access the SMSC number. This is because an iOS device automatically uses the correct SMSC number for your carrier. This information is pre-configured by Apple. So no manual intervention is required.
Pro Tip: Remember that updating an incorrect SMSC number might disrupt your SMS services. In case you are not sure about your SMSC number, it is best to contact your MNO.
Moving on to the next section, we will have a thorough understating of how an SMSC works. Let’s go!
How Does an SMS Center Work?
An SMSC follows a series of steps for its working as described below. Here, I will describe the process in generic and give you a technical sneak peek as well.
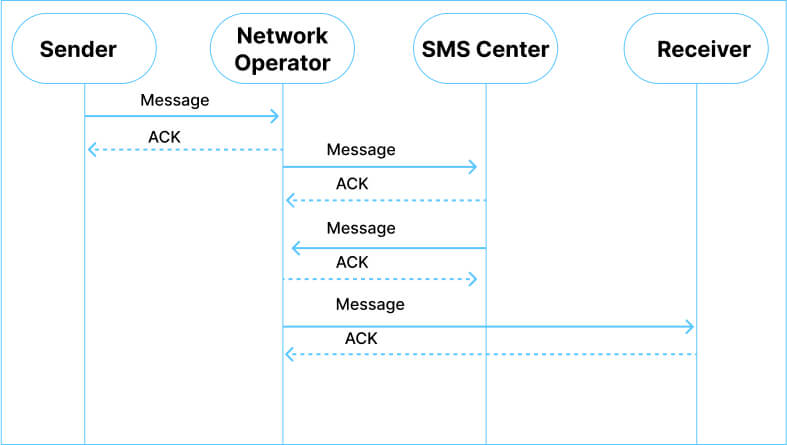
Message Origination
When a user creates an SMS message and hits the send button, the SMS is first received by the SMSC. The SMSC returns a short message to the sender confirming that it has received the message, thus acting as a Temporary Holding Station.
Message Validation
It then checks whether the recipient is available on the same network as that of the sender. To validate, the SMSC analyzes the recipient’s phone number and utilizes its databases like HLR (Home Location Register) and VLR (Visitor Location Register) to identify the associated mobile network. If the sender is not on the same network, then the SMSC forwards the message to another SMSC using protocols like SS7.
Here, the SMSC also performs validation i.e. checking whether the message is properly formatted, its adherence to 160 characters, and correctness of recipient information.
Message is Delivered
The recipient’s network’s SMSC then checks the availability of the recipient’s device. If available, it immediately delivers the message. However, if the device is offline, it stores the message temporarily (typically for 24 hours) and attempts the delivery later.
Delivery is Confirmed
Upon successful delivery of the SMS message, the recipient’s network sends a delivery report to the SMSC which in turn is forwarded to the sender as a confirmation.
An important thing to note here is that all this happens in a matter of seconds and is hardly noticeable by the laymen. Modern-day SMS centers can process up to thousands of messages per second.
Use Cases: Which Industries Require an SMSC Platform?
SMS is a widely popular communication tool across various industries. Here, I am going to mention some of the most prominent sectors that can benefit significantly from SMSC.
Healthcare
SMS is a commonly employed tool in the healthcare industry for various purposes. You must have received appointment reminder texts from your healthcare provider before your visit. And even, receiving reminders about medication schedules is quite common these days. Such texts can be a lot helpful in better management of healthcare centers and improvement in treatment outcomes as well.
Finance

Mobile Banking and Internet Banking are convenient for users to execute transactions. However, to keep such transactions secure, banks use a 2-Factor Authentication mechanism. The process involves sending a security code through a standard text message to the user’s registered mobile number for authenticating logins and transactions.
Besides 2-FA, Payment Alerts are another useful use case where SMSC is critical. Here real-time transaction alerts and account balance notifications are sent to customers. This helps in maintaining transparency and preventing fraud as well.
Bulk SMS Aggregators
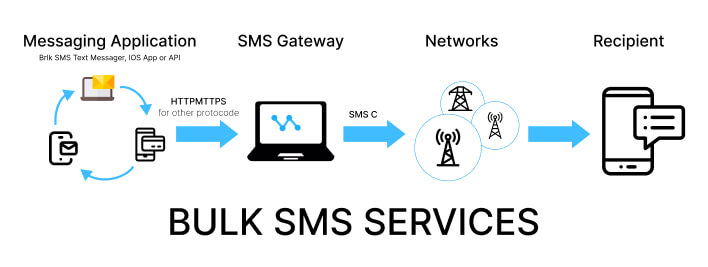
Bulk SMS Aggregators are an important element of the mobile communication ecosystem. They act as intermediaries between MNOs and businesses to facilitate SMS services usually on a larger scale. To ensure the efficiency and reliability of their services, bulk SMS aggregators rely on SMSCs. When a client submits bulk messages through the aggregator’s platform, the messages are queued and communicated to SMSCs. The routing and successful delivery of these messages to individual mobile carriers is handled by the SMSCs.
SMSC Security
SMSCs are critical components of mobile networks that handle sensitive user data and define the integrity of the communication networks. This is why ensuring the security of SMSCs is paramount. Some typical security measures include robust encryption, authentication mechanisms, and intrusion detection to safeguard SMSCs from interception, manipulation, and unauthorized access. Additionally, implementing an SMS Firewall could be an effective security measure to mitigate the potential risks and uphold the trust of subscribers in the integrity of SMS communication.
Future of SMSC
With the rise of RCS i.e. Rich Communication Services and alternative apps like WhatsApp, person-to-person messaging has declined significantly. However, the overall usage of SMS has not declined due to an increase in the use of A2P messaging. According to estimations, the number of A2P messages by 2025 will hit 1.9 trillion.
Rather than being replaced, the probability of SMSC evolving and adapting seems quite high. The emergence of the latest technologies such as the 5G and the IoT are anticipated to derive the demand for effective text messaging services. With this, SMS centers are also going to adapt and evolve. The mobile communication leaps forward with the 5G. The proliferation of 5G devices is going to generate torrents of data including text messages, where SMSCs, with their ability to handle higher volumes of data at blazing speeds, can become as essential units to ensure smooth and efficient delivery of text-based data.
Furthermore, it’s not just about the speed. With the increasing reliance on IoT, text messages can become the primary mode of communication as these IoT devices interact with each other. It can be about anything – from wearables sending health data to automated machines coordinating tasks. While this happens, the SMSCs act as silent translators – ensuring flawless flow of messages between diverse devices, no matter their network or protocol.
Conclusion
An SMSC might appear as a simple messaging router but in reality, SMSCs are powerful engines with solid functionalities. With our exploration of SMSCs through this blog, we have understood the pivotal role of SMSCs in modern communication infrastructure. Their ability to facilitate swift and reliable SMS communication as well as handling massive volumes of messages is truly commendable. While apps come and go, SMSCs are a constant in the communication landscape, always operating behind the scenes.
