
The VoIP industry is passing through a revolutionary phase with new developments in the IP Communications arena. Nowadays, many young entrepreneurs are getting into the VoIP business owing to the boom in this field. The communication business is growing rapidly with the increase in the subscriber base. VoIP Service providers are therefore trying their best to offer quality services by upgrading the existing VoIP infrastructure. In this blog, we are going to dig deep into class 4 vs class 5 Softswitch – two important core components of modern-day VoIP networks. We will also learn about how a softswitch works as a middle device for initiating and routing any call through a telecommunication network.
According to a comprehensive research report by Market Research Future (MRFR), the Global VoIP Market is predicted to reach USD 58.21 billion by 2025 at a CAGR of 12.2%.
What is a Softswitch?

This is one of the most common terminologies of a VoIP business which you might have come across many times. A softswitch is software used in the telecommunication network for launching, maintaining, routing, and terminating sessions in Voice over IP (VoIP) networks. Internet-based telephony and a growing number of traditional telecommunication networks use this software switch to manage the connection of phone calls.
Call switching in the telecommunication industry is a long-term practice to interface the caller to the intended recipient. It was a manual process earlier when the phone administrators shifted the phone line physically, starting with one circuit and then onto the next, to interface the call between a caller and recipient. In the present scenario, if you notice a typical VoIP architecture, the manual call routing has moved on to an automated process with the help of a softswitch.
This software consequently switches the phone lines, and it is a mix of software and switchboard. It has the programmed logic to play out this telephone line exchange. Class 4 and Class 5 Switch are the most widely used switches for routing calls through different networks. Some common types of routing are least-cost routing, loss-less routing, time-based routing, etc.
Class 5 Softswitch
Class 5 Softswitch is a strong platform with lots of interesting modern features. Through this software, a retail VoIP service provider can provide extremely rich quality IP services to enterprise and residential office customers with IP-enabled devices like landline IP phones and adaptors!
Let’s consider a scenario – If an end user wants to make a call from Singapore to Japan PSTN number, what’s the role of Class 5 Softswitch? To begin with, the call controlled by a retail VoIP solution provider will be transmitted to a wholesale VoIP provider via Class 5 Switch. What happens after it reaches the wholesale VoIP provider is explained in the Class 4 Softswitch section.
Characteristics Of Class 5 Softswitch
Class 5 Softswitch characteristics include:
- Call Authentication
It involves confirming the identity of the calling party to ensure that only authorized users can make the calls through the Softswitch.
- Billing and Routing
While billing is all about tracking the usage of services for each user to generate bills, Routing involves determining the most optimal path for a call to reach its intended destination.
- IVR
Interactive Voice Response or IVR refers to the technology that enables automated customer service i.e. computer can interact with humans through voice and DTMF tones input via a keypad.
- Callback
The callback feature allows users to request a callback from the system.
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion
In this process, analog signals or voice signals are converted into a digital format so that data can be transmitted over digital networks.
- Support for Codec & Media Transcoding
Class 5 supports various audio codecs for compression and decompression of audio data. The usage of different codecs has different effects on the quality of the call and bandwidth usage. When 2 communicating parties use different codecs, media transcoding ensures compatibility and seamless communication.
- Social Media Usability
Using this feature, integration with social media platforms can be done. This enables users to call or interact with the softswitch using social media channels.
- Call Transfer
This feature enables a user to transfer an ongoing or active call to another party such as a different department or team.
- Call Holding
The call holding feature allows the user to temporarily put the call on hold, playing some music or greetings, while the user attends to another matter.
- Call Forking
Using this feature, a call can be simultaneously sent to multiple destinations, for instance, when a call is to be answered by multiple parties simultaneously.
Class 4 Softswitch
Class 4 Softswitch is mainly used for routing IP-IP calls to long-distance international locations using an IP network. Now, in our previous example where an end-user wants to initiate a call from Singapore to a Japanese PSTN number, Class 4 Switch will route the call to a Japanese PSTN number only when a wholesale VoIP service provider receives the transfer order from a Class 5 Switch.
In addition, Class 4 Softswitch, which has fewer features than Class 5, enables cost-efficient scaling of voice services while offering a reliable presence between interexchange carriers.
Characteristics Of Class 4 Softswitch
The most important characteristics of the Class 4 solution are:
- Protocol Support and Conversion
To ensure efficient communication between different carriers, class 4 softswitches support various protocols. They also perform conversions to facilitate interoperability.
- Transcoding
This process converts media streams from one codec to another to ensure seamless communication between carriers.
- Calls Per Second Rate
CPS or Calls Per Second Rate is the number of calls a Softswitch can handle per second. It defines the capacity and performance of the Softswitch.
- Average Time of One Call Routing
The average time taken by the softswitch to route a call from source to destination is called the Average Time of One Call outing. This helps in assessing the efficiency of call routing processes.
- Number of Concurrent Calls
Another crucial capacity parameter, the number of concurrent calls refers to the maximum number of calls a softswitch can handle simultaneously.
- Flexible UI (User Interface)
A flexible UI sets up a user-friendly environment for administrators to configure and manage the class 4 softswitch.
- Intelligent Call Routing
This feature dynamically determines the most optimal route for each call.
- Billing Interface Including CDR
The billing interface provides features for tracking and generating invoices. CDR refers to the detailed logs containing information about each call.
- Secured Firewall
The firewall acts as a protective barrier that secures the Softswitch from potential security threats and unauthorized access.
- Filtered Third-party Routing Engine
A third-party routing engine integrated with class 4 Softswitch filters and optimizes the routing of calls, thus boosting the efficiency of the call transit.
Class 4 vs Class 5 Softswitch – Difference Between Class 4 and Class 5 Softswitch
Undoubtedly, both Class 4 & 5 Switches are robust platforms that play an important role in a VoIP infrastructure but, you need to understand some major differences between the two. Here, I have differentiated class 4 vs class 5 Softswitch based on purpose, features, business usage, capacity, and route area.
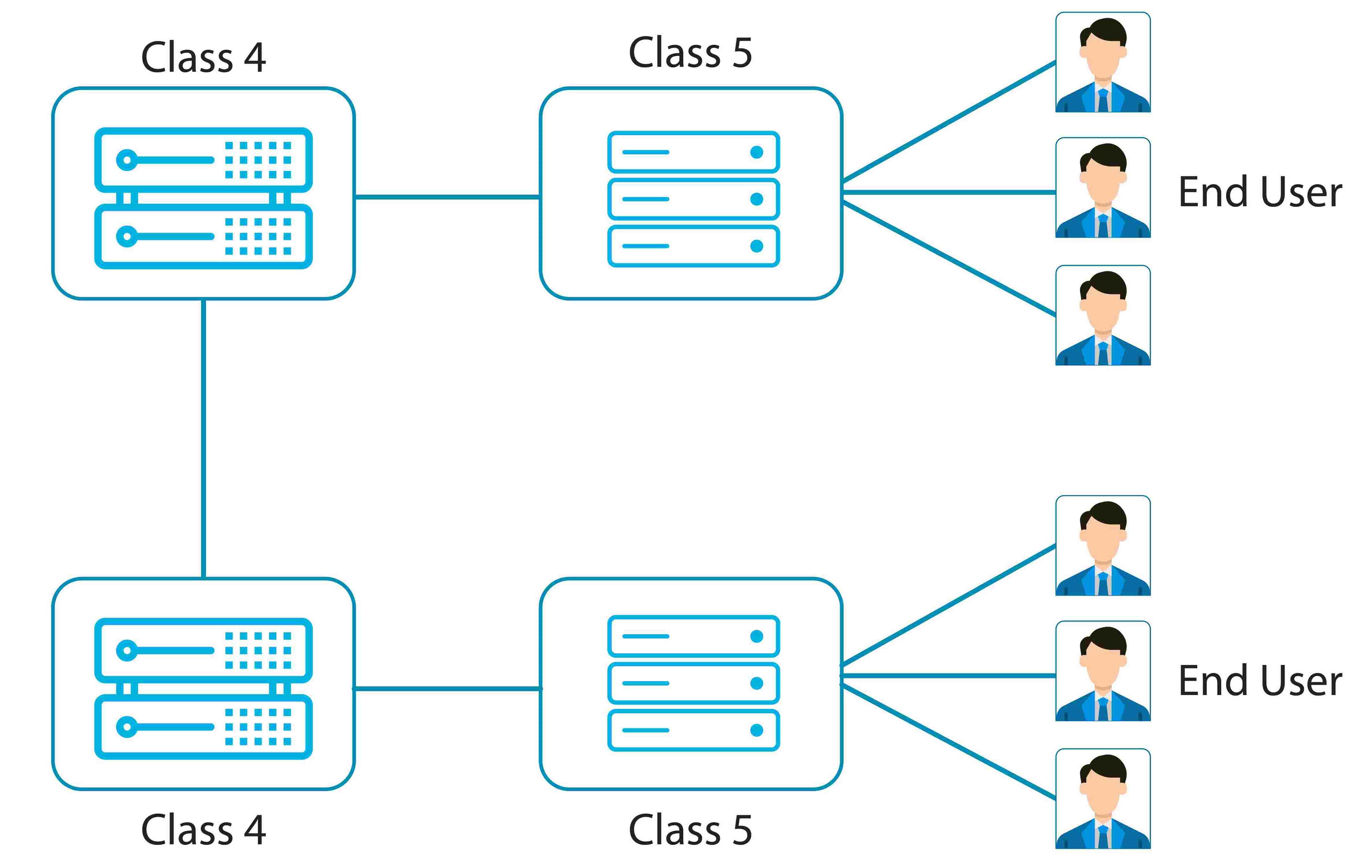
Purpose
Class 5 Softswitch is responsible for transferring calls to Class 4 Softswitch after receiving the calls. It is primarily involved in handling calls within small areas. For long-distance routing through retail VoIP service providers, Class 4 Softswitch comes into action. After receiving calls from Class 5 Switch, a wholesale VoIP service provider routes the call to the long destination with the help of a Class 4 platform.
Features Count
Class 5 Softswitch services include basic dial-tone, calling features, and additional digital and data services to subscribers using the local loop; but a Class 4 Softswitch is just a simplified solution. The main function of the Class 4 solution is the routing of large volumes of long-distance VoIP calls paralleling with other Class 4 telephone switches.
Types of Service
Class 5 Softswitch is more of a retail solution whereas, Class 4 is a wholesale solution. This means a Class 4 switch is a central office telephone exchange that is used to interconnect local exchange carrier offices, for long-distance communications, in the public switched telephone network.
In contrast, a Class 5 Softswitch is a telephone switch or telephone exchange in the public switched telephone network, located at the local telephone company’s central office, directly serving end-users.
Business Usage
Class 5 Softswitches are intended to work with both VoIP service providers as well as end-users. This type of switch platform is for local & long-distance telephony services. So, it possesses additional service features for end-users & corporate clients such as IP PBX features, call center services, calling card platform, types of authorization, QoS, Business Groups, etc.
On the other hand, the Class 4 platform intends to serve wholesale VoIP solution providers, PSTN, Telco Operators, Carriers, etc.
Concurrent Capacity
Class 4 Softswitch can transfer a large number of calls but Class 5 Switch solution can handle a small number of calls, so it is also known as retail softswitch.
Route Area
A Class 4 softswitch routes large volumes of usually long-distance VoIP calls throughout multiple IP networks. In contrast, a Class 5 route calls to the correct IP address, SIP address, or DID number of an End user.
Benefits of Using Softswitch
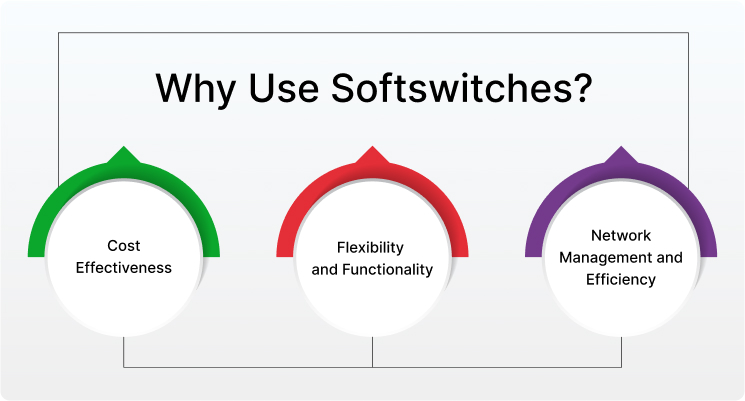
Cost Effectiveness
In terms of cost, softswitches offer savings from various aspects. First, there is no need for expensive dedicated hardware thus saving money on maintenance and space. Second, due to efficient routing and VoIP use, soft switches significantly reduce the long distance and international call charges. Furthermore, when it is about scaling a business, the addition and removal of lines are easy, there is no need for additional hardware investment.
Flexibility and Functionality
The flexibility and functionality offered by softswitches are depicted by 3 main aspects. Softswitches are not just limited to basic call routing. Rather they support a wide range of advanced features such as voicemail, conferencing, and a lot more. Moreover, softswitches perform protocol interoperability i.e. connect different types of networks and devices seamlessly regardless of the underlying protocols. Last but not least, softswitches allow customization i.e. adapt to specific needs and services.
Network Management and Efficiency
Softswitches play a pivotal role in the management of networks through real-time traffic monitoring. These switches provide detailed insights into call patterns and network performance. Moreover, the advanced security features and fraud prevention tools offered by softswitches improve the overall security of the network. When it comes to efficiency, softswitches are easier to update and bug fixes can also be done effortlessly compared to hardware-based switches.
How does VoIP Softswitch Work?
A softswitch functions as the brain of a VoIP network. How? Here’s the breakdown of the inner workings of a VoIP Softswitch:
-
Initiation of the Call
When a number is dialed from a VoIP phone, the phone sends a SIP message to the Softswitch that establishes the call setup process.
-
Routing of the Call
The softswitch receives the SIP message and analyzes its internal routing table. Based on the present information like destination, quality of service, cost, and network conditions, Softswitch decides an optimal path for the call.
-
Call Connection is Established
When the call is within the same network, the softswitch directly connects the users on both ends. If in case, the call is to be sent to an external destination, then the softswitch may need to connect with other softswitches to reach the destination.
-
Media Processing Takes Place
During the call, the softswitch manages the packetization process. It converts voice signals into IP packets for transmission over the network. The softswitch also performs Packet Switching i.e. directs the voice packets through the network, ensuring they reach the destination in the correct order and within an acceptable timeframe.
-
Termination of the Call
When one of the end users hangs up, the Softswitch sends the message to terminate the call. After that, it releases the resources that were used for the call and starts preparing for the next call.
How do Class 4 and Class 5 Softswitch work together?
In today’s modern VoIP networks, class 4 and class 5 softswitches represent two different entities that serve different functions, but they often work in collaboration to facilitate end-to-end voice communication.
When a user initiates a call, the class 5 Softswitch handles the local routing. If the call is to be routed to a distant location, then the class 5 Softswitch hands over the call to a class 4 Softswitch. As the class 4 softswitch takes over, it leverages its advanced routing capabilities and identifies the most cost-effective route for the call to reach its international destination.
iTel Softswitch – Hybrid Softswitch

iTel Switch is a single Softswitch platform for global Retail, Wholesale, Calling Card, and Call Shop businesses. Being a customizable and scalable VoIP Softswitch with integrated billing, it serves as an ideal platform for all VoIP service providers who want to provide VoIP calling services. Multilevel reseller support, easy end-user interface, integrated billing, intelligent routing, and class 4 & 5 Softswitch features are some of the benefits of iTel Switch. If you want a class 4/5 hybrid switch, iTel Softswitch will support your needs as it can handle high-volume traffic. So, if your SIP Softswitch has a higher capacity, it can handle peak-hour calls.
Conclusion
The global softswitch market size was USD 531 million was 2021 and the market is projected to touch USD 870 million by 2031, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.0% during the forecast period (Source). Looking at the statistics, it is evident that investing in innovative communication tools like the class 4 switch and class 5 switch is certainly a wise move. Our industry experts are always ready to assist you with any type of queries you may have.
Looking for VoIP SoftSwitch for Your Business?
Read Also
Features to Look for While Buying a Class 4 Softswitch
7 Benefits of Hosted VoIP Service for Startups
Note: This blog is updated with the latest information and reposted on 29 January 2024.




























Pingback: Features of VoIP Billing Software – REVE Systems()
Pingback: Why a Reliable Softswitch Solution Provider is Important – REVE Systems()