Did you know that “65% of people prefer to contact a business by phone call.”? But what if your business lacks an efficient phone system? In today’s digital age, every business seeks to modernize its communication infrastructure. However, often small business owners get overwhelmed by the options when choosing the right phone system. But fear not! In this blog, we will be discussing all about PBX vs. VoIP, comparing the two most widely used business phone system technologies.
Through this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn about the features, costs, and working as well as the pros and cons of PBX and VoIP. By the end, you will have clarity about which type of business phone system is best suited for you.
We will start with the basics; however, you can also directly jump to the PBX vs. VoIP comparison.
PBX and VoIP are two primary considerations when a business decides to establish its phone system, with each option addressing a unique purpose. Let’s have a look at both:
What is PBX?

A PBX system, or, a Private Branch Exchange System, is a private internal telephone system used by companies and organizations. You can consider it as a ‘mini phone company’ dedicated to managing calls within a company’s network.
It allows for internal communication among employees by providing internal extensions. They can dial appropriate extensions to connect with anyone within the office without needing to go through outside lines. A PBX system also connects employees to the external telephone network either through trunk lines or SIP trunks to receive incoming calls and make outgoing calls.
Types of PBX Systems
Primarily, there are 3 types of PBX systems, differing in terms of characteristics, deployment methods, and features.
-
Traditional PBX Systems
The oldest of them all. Traditional PBX or Analog PBX Systems were hardware-based, consisting of a central switchboard, telephones, and connecting wires. These systems were installed within the premises of the company or organization and required maintenance from IT staff. This form of PBX system was quite reliable but less flexible, expensive to maintain, and lacked advanced features.
-
On-Premise IP PBX Systems
However, as technological advancements took place, IP PBX, i.e. Internet protocol, emerged as the modern take on the traditional PBX. With core functionalities of a PBX, these systems use the internet to transmit voice data rather than using traditional phone lines.
It brought more flexibility and scalability, as well as cost savings for the companies. IP PBX also supports remote work, as employees can use their business phone number from anywhere using an active internet connection. However, an on-premise IP PBX still requires physical hardware to be installed and maintained within the premises.
Insight: IP PBX systems are also known as VoIP PBX. We will understand more about this later in this blog.
-
Hosted PBX or Cloud-Based PBX
The most popular option today is Hosted PBX Systems or Cloud-based PBX. Here the entire hardware and its functionalities, are hosted and managed by a third-party service provider in the cloud. This means that it eliminates the need for any on-site hardware for the company or business.
Hosted PBX is usually available in the form of a subscription. Employees can access the features through a web-based interface. Cloud-based PBX systems offer a wider range of benefits as compared to their predecessors including more flexibility, scalability, advanced features, and a nominal predictable monthly cost.
How PBX Works?
Now that we know the different types of PBX systems, I will be describing the working process of PBX systems depending on the hardware equipment setup. Let’s take a look:
- Conventional PBX phone systems use traditional landline copper wires to make connections. These wires enter a business’s premises and connect to a central PBX box containing telephony switches. These switches are responsible for distributing calls to various phones within the business’s office and provide a limited number of trunk lines (external lines) as well.
- Instead of analog landlines, an IP PBX phone system utilizes digital phone signals to transmit calls. Here, Ethernet cables are used to connect phones rather than traditional phone lines. This also means that there is no need for rewiring. IP PBX systems can be fully on-premise or managed by service providers as well.
- In the case of hosted PBX phone systems, the business needs to pay a monthly subscription fee, which is usually a nominal amount. These services are often suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
Features of PBX
- Internal Extension Dialing: By dialing dedicated extensions, users or employees can reach or connect with colleagues within the organization without using external phone lines.
- Call Transfer and Forwarding: The call transfer feature is useful during active calls when the recipient needs to connect the caller to someone else. In case of call forwarding, the PBX system diverts the incoming call to a predetermined destination number without needing any action during the call.
- Voicemail: The voicemail functionality allows callers to leave their messages in audio format when the recipient is unavailable to take the call and can listen to the message later.
- Conference Calling: Highly useful for collaboration and meetings, the conference calling feature allows multiple users to participate in a single call.
- Call Routing and Queuing: Based on predefined rules and priorities, incoming calls get routed. However, when the lines are busy, incoming calls are placed in a queue until the recipient becomes available.
- Call Logging and Reporting: PBX systems can record call details in the form of CDRs for various purposes, including monitoring, analysis, and billing. PBX systems offer built-in reporting tools or integrate with external software to analyze the collected CDR data and generate corresponding reports.
- Security Features: PBX systems offer security measures like password authentication, firewall integration, and call blocking to restrict unwanted calls, etc. Physical security measures such as locks, access cards, and surveillance cameras are also employed.
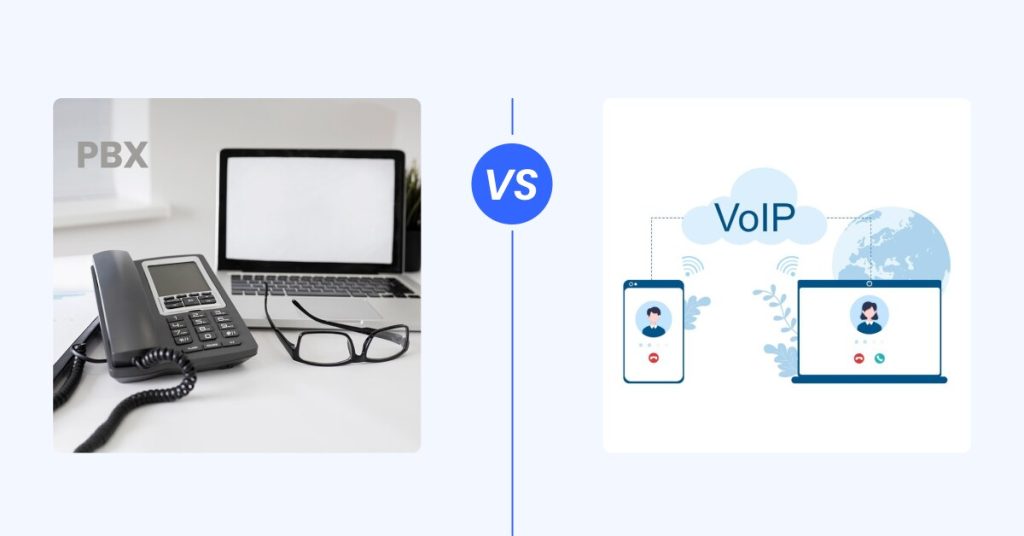
Pros and Cons of PBX
What is VoIP Technology?

Voice Over Internet Protocol is another popular phone system technology. It works by converting analog signals to digital data and transmitting that data over the internet which is then sent to the target phone. Hosted VoIP services are the most popular type of VoIP service where the VoIP provider hosts and manages the VoIP phone system in their data centers.
Let me give you an example for better understanding.
We all know and use classic landline phones. Such a phone uses a physical wire that connects it to the phone company’s network and thus allows users to make and receive phone calls. Now imagine that all these calls are being made using your internet connection instead. This means no physical wires or lines. Voice Over Internet Protocol converts your voice or audio into digital data packets, similar to that of an email or when browsing a website. These digital data packets travel across the internet and reach the destination, i.e. recipient’s phone, where they are converted back into voice.
How Does VoIP Work?
As I have explained above, VoIP takes an audio or voice signal and transforms it into a digital format to make it compatible with traveling over the internet. The data packets that contain information about the voice signal when reach their destination or recipient’s end, the process reverses. In other words, the data packets are decompressed and converted back into analog signals by the device. All this happens so that the recipient can hear the message.
Now you may ask, what kind of equipment is required for VoIP?
Well, there are two must-haves.
1. High-speed Internet: You need a strong and stable internet connection, like a broadband internet connection. This lays the foundation for good-quality VoIP calls.
2. VoIP Phones or Softphones: To make and receive calls, you need a tool, which can be in the form of a VoIP Phone or a Softphone. VoIP phones are similar to landline phones but work by connecting to the internet rather than a physical phone line. Softphone is a software application using which you can make calls from your smartphone, tablet, or computer.
Insight: Softphones, which allow you to make calls over VoIP using a computer, can save businesses $1,727 per month. (Harbor Networks)
The above two, i.e. a strong and reliable internet connection and a phone tool are essential when you want to make and receive VoIP calls. However, several other elements are optional but useful.
- A good quality router can optimize your internet traffic for voice data.
- A headset with a microphone can be quite handy when using VoIP for extended periods or in a noisy environment.
- PoE Switch or Power over Ethernet Switch can be particularly useful to power up VoIP phones directly through Ethernet cables. This eliminates the need for separate power adapters for each VoIP phone.
- If you are using an existing analog phone system for VoIP calls, then you’ll need an Analog Telephone Adapter or ATA. It converts the analog signals from your phone to digital signals so that your traditional phones work with VoIP service.
Features of VoIP
Similar to that of a PBX, VoIP comes with the core calling features, which are:
- Crystal Clear Calls
- Call forwarding
- Call Recording
- Caller ID & Call Waiting
- Conference Calling
- International Calling
Advanced Features of VoIP
- Auto Attendant: It’s the virtual receptionist who greets the callers with a professional message and directs them to the appropriate destination.
- IVR or Interactive Voice Response: Using the IVR feature, automated menus can be created that allow callers to navigate your phone system by choosing appropriate menu options using voice commands.
- Voicemail to Email: Voicemail messages received by a VoIP phone can be transcribed into text and delivered straight to your email inbox.
- Call Queuing: To manage high call volumes, callers can be placed in a queue and routed to available agents based on the order in which they arrive.
- Click to Call: It allows users to initiate phone calls directly from a website or app by clicking a button or link. This saves customers from manually dialing the phone number thus saving time and reducing errors.
- Call Analytics: VoIP systems collect call data such as date and time, caller ID, phone number, call duration, etc., and generate detailed reports and insights. This helps identify call trends, and areas for improvement, check the effectiveness of campaigns, and track employee performance.
- Encryption: By implementing encryption algorithms that scramble the voice data during calls, VoIP systems can make calls unreadable to anyone who intercepts the calls. Only authorized parties with a decryption key can unlock and understand the conversation.
- Spam Call Blocking: This feature helps in identifying and blocking unwanted robocalls and telemarketing calls. It works by checking the caller ID against the database of known spam numbers. Users benefit as it reduces interruptions and saves time to focus on important calls.
Leveraging all these features, VoIP phone systems empower businesses to streamline their communication, improve customer service, and enhance overall collaboration.
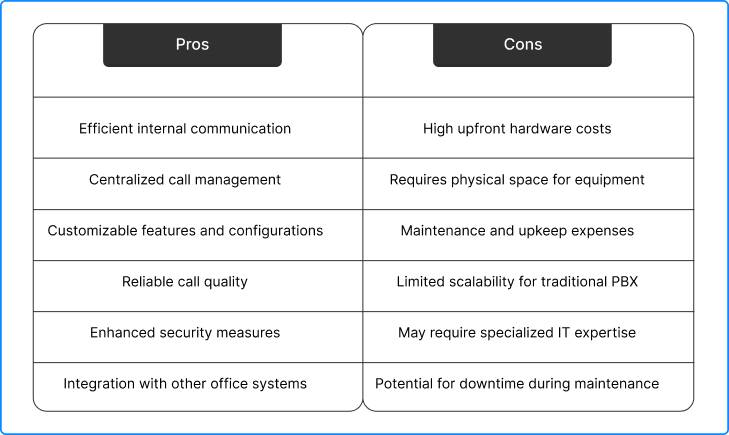
Pros and Cons of VoIP
PBX vs. VoIP: Key Differences Between PBX and VoIP
Over 90% of businesses rely on their phone systems as their main communication tool. More than half use phone calls to make sales, while 43.6% prefer phone calls to provide customer service. These facts further emphasize the importance of understanding and choosing the right telephone technology for any business. By now, we have thoroughly understood the two major phone technologies, i.e., PBX and VoIP. Let’s move further and compare both, i.e., PBX vs. VoIP, to know which technology best fits your business.
1. Setup and Maintenance Cost

Cost is a significant factor to consider when installing PBX vs VoIP.
PBX systems require a substantial upfront investment for hardware like routers, servers, and gateways. Apart from the cost of phone lines, power supply as well as installation and infrastructure setup costs are also there.
Whereas in the case of VoIP, the upfront cost is only in the form of a nominal monthly subscription. This monthly charge is usually dependent on the plan you choose. The user company only needs a stable internet connection and phones (VoIP phones or software).
The average savings businesses saw after switching to VoIP was 50%-75%. Specifically for small businesses, VoIP systems save about 45% each month on communication costs compared to traditional phone systems. (Multicomic, 2021)
In terms of maintenance, which is an ongoing cost, PBX systems require dedicated IT staff because of their complexity. On the other hand, VoIP is typically managed by a third-party service provider, reducing the IT burden for your company.
2. Scalability

Often, businesses ignore the importance of considering the scalability factor, i.e., growing their business.
Scaling or expanding a PBX system is usually accompanied by the purchase of new hardware to install new phone lines. This process can be quite time-consuming and expensive, especially when you are shifting your office to a new location. This will mean that you have to build and install the whole PBX system from the very beginning and need a new module to add extra phone lines.
However, with VoIP, all this trouble gets eliminated because it scales easily by adding users or features to your existing plan. You’ll only need to get some more IP phones and maybe increase your internet bandwidth as well.
VoIP again shines in terms of scalability.
3. Features and Functionality

The conference call feature is one of the top VoIP features cited as increasing productivity by 65% of small businesses. (Startupanz)
I have already mentioned that both PBX and VoIP offer standard calling features; however, VoIP boasts a wider range of advanced features. Many VoIP plans usually include video conferencing, instant messaging, CRM integration, and detailed call analytics. VoIP also offers apps that boost remote work flexibility.
PBX again lags in terms of features and functionalities. Since PBX systems are location-dependent, they do not support remote work. Also, when it comes to mobile integration, PBX systems typically require special mobile apps.
4. Security and Reliability

This is another important area of concern as we are comparing PBX vs. VoIP.
PBX systems are based on on-site hardware, such as a traditional PSTN, and not an internet connection. This adds to their reliability and security, as there is no risk of internet-based threats. However, PBX systems may become unreliable in the following situations:
- Power outages
- Physical intrusion
- Hardware failure
On the other hand, VoIP systems are susceptible to cyber threats and attacks. This makes VoIP security a topic of concern for businesses around the world
However, VoIP providers often follow the latest and most robust VoIP security techniques, including:
- End-to-End Encryption
- Real-time Network Monitoring
- 2 Factor Authentication
- Firewall Protection
Besides all of the above, VoIP providers employ third-party security and compliance certifications like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI, SOC 2 Type 2, etc.
VoIP systems come with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery features in disaster recovery, while with PBX systems, this can be complex.
5. Call Quality

In its early days, VoIP calls suffered poor call quality, which is why PBX remains a preferred choice for many businesses. But nowadays, the scenario has changed. VoIP offers HD audio and video, which makes it way better than traditional phones.
While PBX systems are established to provide good call quality, they come with a downside, i.e., dependency on hardware infrastructure. Any issue that may arise in the hardware setup can affect the quality of the calls.
On the other hand, VoIP is reliant on internet technology, which, again, if not stable, can cause drops in the call. However, VoIP providers these days maintain a backup power supply and sufficient internet bandwidth so that no glitches happen.
Now that we have discussed the 5 key aspects of PBX vs. VoIP, we will quickly look at various other factors where PBX and VoIP differ.
-
Suitability
Due to hardware requirements and high upfront costs, PBX systems are suitable for large organizations that have sufficient resources to invest in them. VoIP scales effortlessly and costs reasonably, which makes it an ideal fit for companies of all shapes and sizes, especially small businesses.
-
International Calls
Calls made over long distances often come out to be expensive when made through PBX systems. On the other hand, VoIP makes it significantly cheaper.
-
Customization
PBX systems offer limited and complex customization and require technical expertise as well. In the case of VoIP, online portals make it an easy job.
What is a VoIP PBX Phone System?
Companies with existing PBX systems can migrate to a VoIP PBX system as it offers several advantages over their current setup. The transition can be done by following any of the two approaches:
- SIP Trunking, where traditional phone lines are replaced with SIP trunks that connect PBX to PSTN via the internet. The company can leverage the cost benefits of VoIP for outgoing calls while still utilizing PBX for internal calling.
- Another way is to gradually replace traditional desk phones with IP phones that directly connect with the VoIP network. This approach eliminates the reliance on PSTN while enabling users to fully access VoIP features.
Choosing Between PBX vs. VoIP: Top 3 Considerations
What’s your Business Size, Type, and Budget?
For big companies that have sufficient resources and dedicated IT staff, PBX can be a good option. With PBX, they will be able to get high-class call quality. But if you are looking for an affordable, flexible, and efficient solution that doesn’t burn a hole in your pocket, then VoIP is for you.
If your business follows the remote working model, then you must choose VoIP because of its flexibility.
What All Features Do You Need?
Suppose you are a small business with just a few employees and require basic calling features, then PBX sounds like a good option for you. However, you must keep the growth factor in mind, i.e., as your business expands, you will need more phone lines and advanced calling features. With a traditional PBX setup, upgrading could mean a heavy investment.
On the other hand, VoIP gives you the flexibility to start with a basic plan if your requirements are simple. And you can always upgrade later without investing too much or wasting any resources.
So choose your option wisely.
What About Your IT Expertise?
Companies with teams of technically skilled personnel can think about the installation and setup of PBX systems. However, if you are a business with limited resources, then it is best to go with VoIP.
It may be a good idea to take some time and analyze the availability of your resources, make estimations about your budget, and think about your actual requirements.
Last Words: Which One is Better, PBX or VoIP?

We have learned that both PBX systems and VoIP systems have their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
While PBX is a reliable and secure technology for phone communication, it has the major drawbacks of high upfront and maintenance costs. Plus, scalability is another issue for businesses seeking rapid expansion.
On the other side, VoIP offers more flexibility and scalability, and it comes with the added advantage of a lower cost or investment. According to productivity statistics, VoIP features improve small businesses’ productivity by 77%. (CISCO, 2021)
The only factor that could affect the performance of a VoIP system is the quality of the Internet connection. However, in today’s age of the internet, this is not an issue anymore.
With this, our debate between PBX vs. VoIP comes to an end. Whichever option you choose for your business, remember that investing in a robust communication infrastructure is vital for staying competitive in today’s interconnected world.