Statistics reveal that “In 2022, SIP accounted for over 60% of all business voice traffic.” Furthermore, studies also reveal that “By streamlining communication pathways, SIP is projected to save companies up to 50% on their telecommunication expenses by 2024.” This percentage signifies the dominance of SIP in handling business phone calls. Let’s visualize that you are on a call with your overseas client using your laptop. Now you rush to meet a family friend, transitioning seamlessly to your mobile while being still on call with your overseas client. Do you wonder who works silently behind this seamless flow of conversations? For the next few minutes, you will read everything about the Session Initiation protocol i.e. SIP.
As we step into the world of SIP, we will explore the different layers of SIP, learn about its functionality, and its significant role in the modern communication landscape.
Let’s get started!
What is Session Initiation Protocol?
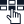
Session Initiation Protocol or SIP is one of the most common signaling or telephony protocols. It is used for establishing VoIP sessions i.e. voice and multimedia communication sessions in real time over the internet protocol or IP. In other words, we can say that SIP is a method of deploying VoIP. One important point to remember is that SIP is media independent which means it doesn’t work specifically for voice, video, and data, but for any type of communication.
For better understanding, let’s break down the protocol:
Session
When we refer to a session, it is nothing but a call between two endpoints. This call can be a phone call a video chat or an instant messaging conversation between two parties. For example, two users connected over a video call using a communication app like Zoom. Such a communication session is facilitated by SIP.
Initiation
As the term indicates, initiation refers to the commencement of a Session. For example, a user initiates a call by clicking the Call button on a VoIP app. Here SIP protocol is used to establish the connection.
Protocol
The rules and conventions based on which communication happens between devices or systems is the protocol. Here SIP sets the standard for signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions. For example, when a call is set up, the SIP dictates how devices will communicate with each other.
Important Protocols Related to SIP
It is important to note that SIP does not work alone, but rather in conjunction with several other protocols which are as mentioned below:
1. SDP i.e. Session Description Protocol
The basic purpose of SIP working in conjunction with SDP is to describe and negotiate multimedia sessions between the participants of the call. So when a communication session is established, SIP uses SDP to specify the details of media types such as audio and video codecs, bandwidth requirements, etc.
2. RTP i.e. Real-Time Transport Protocol
SIP uses RTP to transport media streams such as audio and video data during a communication session in real-time. This is done to ensure timely delivery, sequence numbering, and other crucial aspects of real-time communications.
3. HTTP i.e. Hypertext Transfer Protocol
Some networks do not approve of direct SIP traffic. In such scenarios, SIP traffic is encapsulated within HTTP packets so that they can pass through the restricted networks without any difficulty.
4. Domain Name System (DNS)
For call routing and endpoint identification, SIP needs to resolve domain names to IP addresses. This is where the role of DNS comes in. So when a SIP call is initiated using a domain name, the DNS performs the job of resolving this domain name to a corresponding IP address.
5. Transport Layer Security
To maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the data exchanged between communication sessions, SIP makes use of TLS. This layer safeguards sensitive information such as user credentials from being tampered with and eavesdropped.
Brief History of SIP
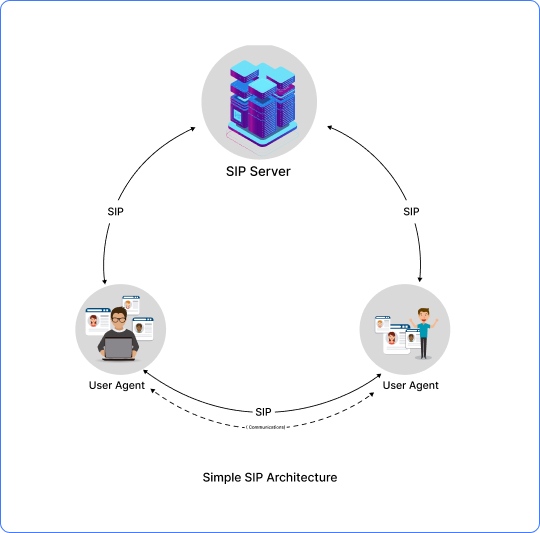
In the late 1990s, the IETF i.e. Internet Engineering Task Force identified the need for a standard system for the management of online communication. Learning from the already established protocols like HTTP and SMTP, the tech experts at the IETF developed SIP.
Initially, SIP was tailored for VoIP, enabling users to make voice calls online. However, the versatility of SIP quickly became apparent. Soon after, SIP became the ‘Foundational Communication Framework’ for video conferencing, instant messaging, and online gaming. Then in 1999, the IETF formally standardized the SIP through RFC 3261.
Since then, SIP has been on a continuous evolution to address the emerging communication needs in the ever-changing landscape of modern communications. The above image depicts the key developments that happened in the SIP landscape.
Key Features of Session Initiation Protocol
Now that we know a bit about the session initiation protocol, the next thing I would like you to know are the features offered by this protocol. These features enable various aspects of real-time communication across different devices and platforms. Let’s understand some of the key features of SIP.
Session Establishment and Termination
A key feature of the SIP protocol is that it enables the establishment, modification, and termination of communication sessions between users. For instance, when a voice or video call is generated using an SIP-based app such as WhatsApp, the protocol initiates the connection between the call participants. It allows users to connect, communicate, and terminate the call when completed.
User Location and Registration
With the help of SIP, users can register their location and availability which makes it possible to determine their location and be reached. Let’s consider the case of a business where SIP-based phones can register their location with a SIP server. When an extension is dialed, the registered SIP device is located by the SIP server and the call is established.
Call Routing and Forwarding
The call routing and forwarding feature of SIP enables users to redirect their calls to different devices or phone numbers. This feature is quite valuable when a call goes unanswered on a SIP-based phone and gets automatically forwarded to another number, device, or voicemail.
Conferencing
Another useful feature of SIP is that it supports multi-party communication or conferencing. Popular services like Zoom or Microsoft Teams leverage SIP for video conferencing where multiple users can join a video call in real-time.
Media Negotiation and Handling
SIP telephony protocol negotiates various parameters of a communication session including codecs, bandwidth, and media capabilities. For instance, when communication happens between two devices using Session Initiation Protocol, they ensure the highest quality communication by negotiating the best codecs for audio and video.
Presence Information
This feature conveys the availability and presence of the users. For instance, in messaging apps like Skype, SIP can convey whether a user is online, offline, or busy.
SIP Trunking
One of the most valuable features of SIP is trunking. This service feature leverages the SIP to establish virtual connections between a PBX and the outside world. A SIP trunk serves as a digital bridge, linking a company’s internal phone system (PBX) with external networks. By harnessing SIP, it facilitates the smooth transmission of voice, video, and data over an IP network. This modern solution is not just cost-effective but also easily adaptable, replacing conventional phone lines while offering scalability to meet evolving communication needs.
How does SIP work?
SIP is an application layer protocol that works with several other protocols of the application layer to perform its functioning. An interesting point to know here is that SIP is very similar to HTTP i.e. Hypertext Transfer Protocol. From being text-based protocols to relying on headers to convey important information and following client-server architecture – these are some major similarities in design between Session Initiation Protocol and HTTP. These similarities lead to better interoperability between systems that use SIP and HTTP. This also eases the integration of SIP functionalities into systems that are already built around HTTP.
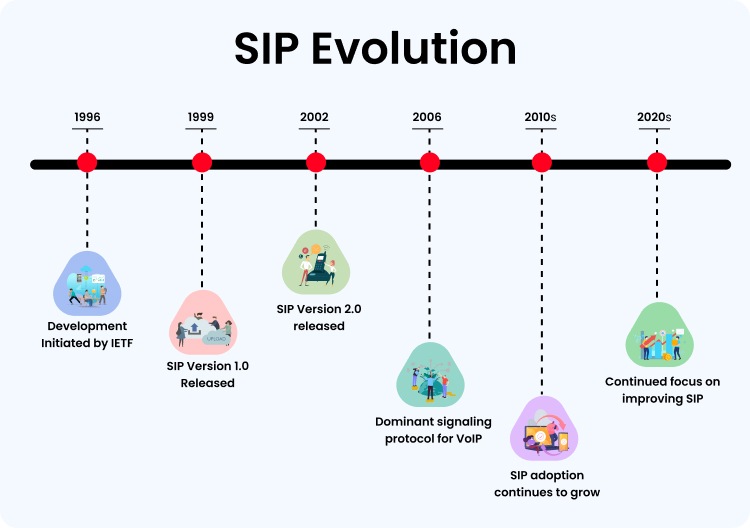
A simple session using SIP consists of the following.
- The Session gets Established
- Communication takes place
- The Session gets Terminated
Let’s understand the SIP Call Flow in more detail:
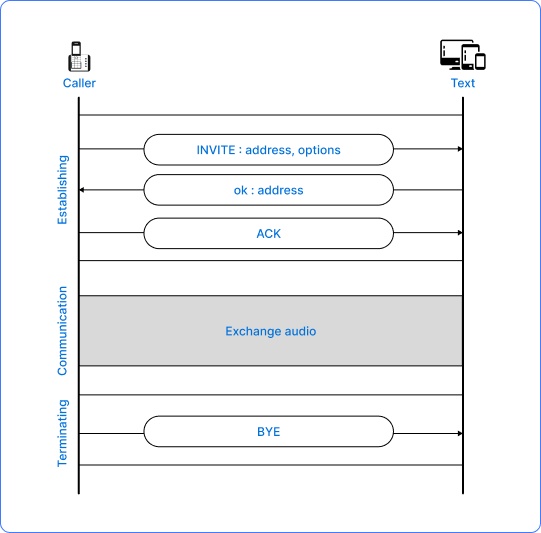
A user dials a phone number and initiates the call flow.
- This call initiation request is sent to an SIP server.
- This SIP server then identifies the SIP address of the other user. Upon identification, it sends an invitation to the other user.
- When the invitation is accepted, the connection is established and communication begins.
- As the communication happens, audio and video data are exchanged between the two endpoints.
- When the call is finished, the SIP server communicates to the other to tear down the call.
Examples of SIP
Before we delve more into Session Initiation Protocol, let’s quickly take a look at some real-life examples where SIP is used:
Managing Customer Queries at Contact Centers
SIP-based solutions are extensively used in contact centers to handle customer interactions. Various features of SIP including call routing and call queue management help in enhancing the efficiency of customer support services.
To Provide VoIP Services
To offer VoIP services, Telecom service providers leverage SIP in their infrastructure. SIP facilitates incoming and outgoing calls over the Internet along with various features such as voicemail and conferencing.
For Business Communication
Another area where SIP is extensively used is the business environment. Organizations deploy SIP-based PBX systems for seamless internal and external communication. Softphones are commonly used within organizations to communicate and collaborate.
Benefits of SIP
SIP benefits businesses by improving communications and streamlining operations in several different ways.
Cost-effectiveness
Session Initiation Protocol routes call over the internet, which means it leverages existing internet infrastructure. Thus there is no need for separate networks for voice and data which reduces communication costs.
For example, an MNC employing SIP-based VoIP can save significantly on long-distance calls as calls travel over the Internet rather than on traditional telephony.
More Scalability
Businesses often need to add or remove users as per their changing business requirements. SIP easily adapts to the growing and shrinking demands without any extensive infrastructure changes. For example, A budding startup firm can easily expand its communication infrastructure and meet its evolving needs by adding new phone lines using SIP-based phone systems without investing much resources in setup procedures.
Unified Communications
The ability of Session Initiation Protocol to support various forms of communication such as voice, video, messaging, and more into a single, cohesive platform enabling unified communication boosts collaboration and productivity to a different level. For example, an organization with SIP-based unified communication solutions can share documents, do video conferences, and engage in real-time chats from one platform fostering seamless collaboration among employees and helping them stay productive.
Enhanced Mobility
Using SIP, users can seamlessly switch between devices and locations anywhere with an internet connection. For example, a sales team can stay connected on the go and forward calls from one line to another using SIP-based services. This ensures that crucial client conversations happen seamlessly.
Enhanced Features
With the use of SIP, businesses can enjoy advanced communication using features like call forwarding, voicemail-to-email transcription, and a lot more. For example, Voicemail messages can be sent as email attachments or written messages for easy access.
Better Reliability
Session Initiation Protocol enables automatic rerouting of calls to alternative devices in case of service disruption or outages. The redundancy and failover capabilities of SIP ensure business continuity during such scenarios. For example, a call center business can ensure continued customer support using SIP-based communication. Calls can be rerouted to available agents in different locations when downtime happens.
Difference between SIP and VoIP
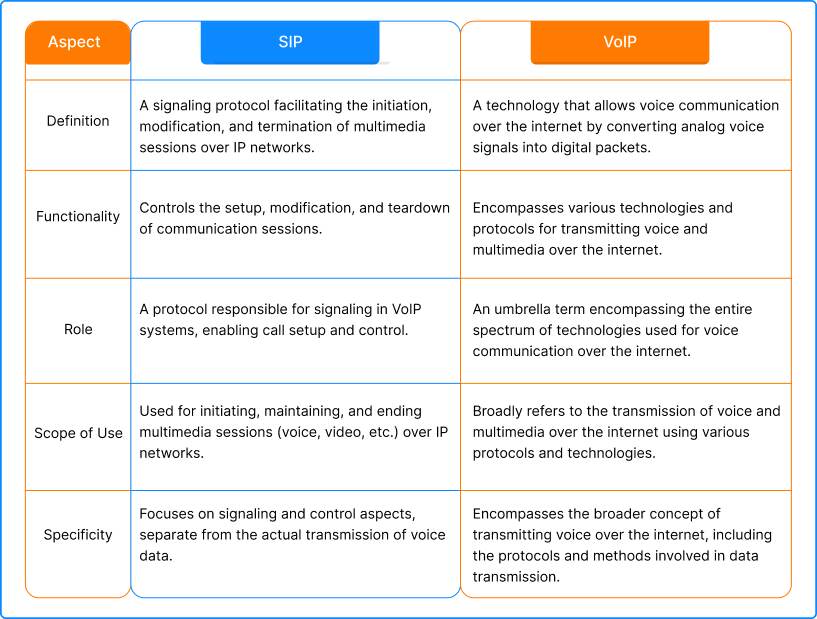
In telecommunications, VoIP and SIP are often thought of as similar, however, these are two different concepts. Let’s understand each other through some examples.
VoIP or Voice of Internet Protocol is the technology that is used to make voice calls over the Internet instead of using the conventional telephone system. The working of VoIP involves converting audio signals into digital data packets which are transmitted to the destination over the internet. VoIP communication goes beyond VoIP; it supports video and multimedia messaging as well. For instance, when you make calls using WhatsApp or Google Voice, you make calls using the VoIP technology.
Now, let’s understand how Session Initiation Protocol is related to VoIP. The SIP protocol is used to establish, modify, and terminate real-time sessions. These sessions involve different multimedia elements including voice, video, chat, gaming, etc. The working of SIP involves setting up and managing communication sessions. This protocol allows devices to initiate and terminate communication sessions and negotiate the parameters as well.
Often session initiation protocol is used in conjunction with VoIP. For instance, you make a voice or video call using a VoIP application like Zoom App, where SIP might be the protocol that sets up and manages that call.
How to Get Started with SIP Telephony?
Now that you are familiar with the session initiation protocol, we will understand how a business can get started with SIP telephony.
- To avail of SIP telephony services, the first thing you need to do is – select a SIP Provider. Research and choose the one that best suits your needs in terms of reliability, features, scalability, and pricing.
- To use SIP telephony, you need access to SIP-compatible devices such as a softphone. If you want to use SIP on your existing analog phone then you’ll need adapters.
- Once ready, you can start creating and configuring your account on your devices. The credentials such as username, password along with server details will be provided to you by your chosen SIP provider.
- To test connectivity and functionality, you can start making calls. Also, it is time for you to explore additional features such as voicemail, call conferencing, call forwarding, etc.
- It is always recommended to monitor the performance of your SIP telephony setup and optimize configurations as required.
Conclusion
The global session initiation protocol (sip) trunking services market grew from $14.69 billion in 2022 to $16.49 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3%. is expected to grow to $26.82 billion in 2027 at a CAGR of 12.9% (Source ). With these statistics, we conclude that SIP is a future-proof protocol and will be leveraged by more and more organizations around the world in the coming time.