What is a Softswitch? Working, Types, Benefits & Use Cases
- July 21, 2025
- 16 Mins Read
- Listen

Today, VoIP is the most revolutionary communication technology that enables us to make and receive calls over the Internet. But who’s the powerhouse behind the revolutionizing VoIP technology? It’s the Softswitch! From managing the call setup, finding the best call routing path, and connecting the call within or across networks, a Softswitch ensures that VoIP calls are crystal-clear and uninterrupted.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through the different aspects of a softswitch – what is a softswitch, how does a softswitch work, class 4 vs class 5 softswitch, along with some real-world use cases. I’ll also introduce you to our powerful softswitch products, i.e., REVE Session Border Controller (Class 4 Softswitch) and iTel Switch (Class 5 Softswitch).
What is a Softswitch?

Softswitch is short for Software Switch, which is a core component used in telecom networks for call control and signaling as well as processing media streams. In layman’s terms, we can define softswitch as a software application that manages the connection between phone calls placed over the internet, i.e., VoIP calls. Acting as a bridge, a softswitch directs and controls the flow of voice, data, and multimedia sessions across IP networks.
How is a Softswitch Different from a Traditional Switch?
The primary role of any switch is to facilitate communication, but what makes the modern-day softswitch more versatile? It’s their software-based nature. I will explain this with the help of 3 key aspects as mentioned below:
Hardware vs Software
A traditional switch is a dedicated hardware system that makes use of circuit switching to connect calls physically. This is why traditional switches are also called hardware-based switches or circuit-based switches. These switches require manual configuration for their work. On the contrary, a software-based switch makes use of digital signals to route calls digitally or over IP networks.
Rigidity Vs Flexibility
The conventional circuit switches get obsolete with time and need additional hardware for working in line within the modern communication landscape. On the other hand, softswitches are quite flexible and offer a wide range of features such as call recording, voicemail, conferencing, etc.
Expensive vs Cost-effective
Traditional switches are expensive to maintain and upgrade, whereas softswitches run on standard infrastructure, making them a cost-effective and easier-to-maintain and upgrade option.
How Does a Softswitch Work?
To understand the workings of a softswitch, let’s consider an example. Your phone rings, and you pick up the call and start your conversation with the other person on the call by saying Hello. From this very moment, the role of a softswitch comes in, and there are several key functions performed by a softswitch. These functions are:
Call Routing
The softswitch makes sure that each call reaches its intended destination following the most optimal route or path. To identify an optimal path, a softswitch considers various factors like network congestion and quality, etc.
Protocol Conversion
To ensure seamless communication across diverse networks, softswitches convert voice signals from analog to digital and manage protocol conversion that governs the respective communication.
Call Management
There are 3 key processes handled by Softswitches – Call Setup, Teardown, and Authentication. By overseeing these processes, softswitches ensure quality and security during the communication sessions.
Softswitch System Architecture
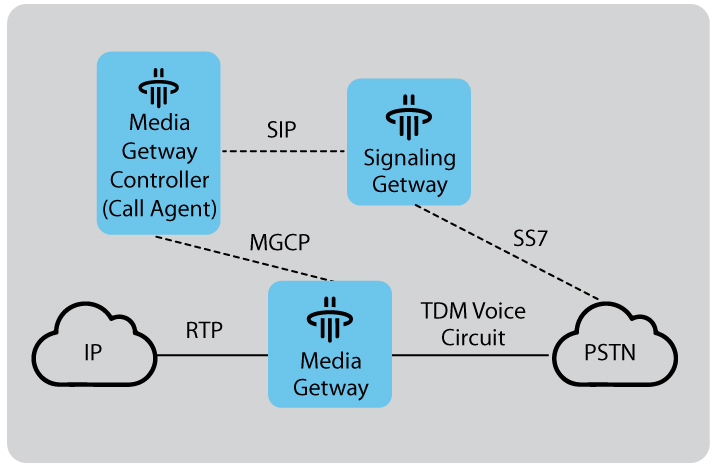
The above image represents a typical setup of a softswitch system. Now, I will take you through the different components of a softswitch, one by one:
Media Gateway Controller: The Brain of the Softswitch
MGC or Media Gateway Controller is responsible for call control and signaling intelligence. From managing call setup, routing, features, and billing, along with interactions with other networks, all this is handled by MGC. Furthermore, this key component makes use of protocols like SIP or H.323 to communicate with other softswitches and gateways.
Media Gateway
It is responsible for the physical media conversion and transmission of voice and data traffic. Media Gateways take instructions from Media Gateway Controllers, i.e., MGC, and send call status updates.
Signaling Gateway
SGB or signaling gateway bridges different networks by acting as a translator for signaling protocols. It makes use of various signaling protocols to connect the softswitch with external networks. Furthermore, it is responsible for converting signaling messages between different protocols to maintain interoperability.
Types of VoIP Softswitch
VoIP softswitches are categorized into 5 main types, with each softswitch performing a different functionality.
Class 1 Softswitches are implemented in international gateways, i.e., handle high volumes of long-distance calls across different countries and continents. They are designed for wholesale carriers, managing large-scale traffic between various telecom providers. Class 2 softswitches focus on regional traffic, i.e., handling traffic between local carriers. Class 3 Softswitches are often used by ISPs to connect with larger carrier networks or the PSTN.
Now comes the most widely deployed softswitches, i.e., Class 4 and Class 5 Softswitches. Let’s understand what these are.
What is a Class 4 Switch?
Class 4 switches are used for handling long-distance or wholesale VoIP traffic. You can imagine it as a highway for large volumes of call traffic that efficiently optimizes geographically distant connections. The main perspective behind using Class 4 Softswitches is cost-effective routing and traffic management. Key features offered by Class 4 softswitches are:
- Concurrent calls
- Protocol support & conversion
- Intelligent call routing
- Secured firewall
- Easy to use and simple interface
What is a Class 5 Switch?
Class 5 Switches are focused on providing service to end users or subscribers, such as residential clients. Class 5 softswitches are mostly used by ISPs or telecom companies to manage local calls. That being so, class 5 softswitches are used to offer smaller volumes of call traffic and to offer personalized services to clients.
- Auto-attendant
- Call forwarding
- Call transfer
- Call waiting
- Caller ID
- Conference calling
- Virtual phone numbers
Class 4 Softswitch vs Class 5 Softswitch
Both classes of softswitches play a significant role in VoIP networks. The difference between a class 4 and a class 5 switch can be marked based on 2 key areas:
- Focus
Class 4 softswitches are designed for wholesale carriers and service providers to handle long-distance traffic. On the other hand, Class 5 softswitches cater to end users.
- Volume Handling
Class 4 softswitches specialize in handling high call volumes across geographically diverse locations, also called interexchange VoIP traffic. In contrast, Class 5 Softswitches handle smaller yet diverse call traffic within a specific geographic area.
To understand the difference between the two softswitches in a better way, I have created this comparison table. Take a look:
|
Feature |
Class 4 Softswitch |
Class 5 Softswitch |
|
Primary Role |
Wholesale call routing, inter-carrier traffic |
Retail call management, end-user services |
|
Target Audience |
Large-scale VoIP providers, telecom carriers |
Businesses, individual end-users, residential customers |
|
Call Volume |
Handles large volumes (millions) of concurrent calls |
Manages smaller volumes, focused on local calls |
|
Geographic Scope |
Long-distance, international, inter-network routing |
Local, metropolitan, regional routing |
|
Key Functionality |
Least Cost Routing (LCR), protocol conversion, transcoding, intelligent routing, billing interface, security, concurrent call management |
IP PBX features, voicemail, call forwarding, IVR, conferencing, caller ID, call waiting, e-911, call recording, billing, authentication, virtual numbers |
|
Focus |
Cost-efficiency, high-volume traffic, global reach, carrier-grade reliability |
Feature-rich user experience, advanced telephony services, localized solutions, business continuity |
|
Interconnection |
Connects to multiple carriers and media gateways |
Connects end-users’ devices (phones, IP PBXs) to the network |
|
Example Use Cases |
International call termination, carrier interconnect agreements, wholesale VoIP business |
Business phone systems, hosted PBX services, calling card platforms, call centers, unified communications (UCaaS) |
|
Billing Complexity |
Primarily focuses on wholesale billing and CDRs |
Offers more granular retail billing models (prepaid, postpaid, hybrid) |
|
User Interface |
Often more technical, focused on network management |
Typically more user-friendly, with admin and end-user portals |
|
Service Level |
Provides basic connectivity and routing |
Offers advanced features directly to the end-user |
Benefits of Using Softswitches
Businesses and organizations around the world have observed several benefits of using softswitches.
1. Scaling Up and Down is Easy
Softswitches offer incredible scalability. Because softswitches run on software, adding more calls doesn’t require any type of physical expansion. Softswitches facilitate scaling up and down virtually.
If you wonder who can benefit from the scalability of softswitches, then startups, call centers, cloud providers, etc., are a few businesses. The scalability of softswitches can help such businesses adapt to changing business needs.
2. High Reduction in Cost
When compared to traditional circuit-based switches, softswitches come out to be quite pocket-friendly. Since there is no additional hardware to be purchased for the working of softswitches, companies save a lot of money. Even when there’s a need to upgrade, softswitches allow so this without any heavy investment.
3. Automate Accurate Billing
Traditional switches relied on manual billing, which is prone to errors. However, modern-day softswitches have automated the whole process as they come with built-in billing solutions. Softswitches are capable of tracking call details in real-time with laser precision and applying pre-configured billing rules to calculate tariffs and generate accurate invoices.
Beyond billing accuracy, softswitches offer a lot of convenience and add efficiency to the overall communication process. Both businesses enjoy faster and transparent invoicing, which ultimately builds the trust of the customers. Mobile operators leverage softswitches to ensure accurate billing of prepaid, postpaid, data usage, and roaming charges.
4. High Versatility
It won’t be an overstatement if I say that a softswitch is a universe of possibilities. Don’t believe it? Let me explain.
The first reason for the above statement is that Softswitches handle Multiple Services under One Roof. From voice calling, video conferencing, and instant messaging to unified communications platforms, Softswitches can handle them all.
Secondly, softswitches can seamlessly adapt to any technology, be it VoIP, traditional PSTN, or a combination of both. This adaptiveness of softswitches makes them a universal element of the telecommunication world.
Last but not least, modern-day softswitches come like a tailor-made suit for your communication requirements. They can be customized with a wide range of features to fit your business’s unique needs.
5. More Reliable
Softswitches have in-built real-time monitoring capabilities, using which they actively monitor QoS. In instances when there is a sudden increase in call load, the softswitch can automatically make real-time adjustments to its configurations. This is done to ensure that communication happens without any glitches.
VoIP Softswitch Use Cases
Softswitches are deployed extensively across various sectors and industries. Here are real-life use cases for the same:
1. OTT VoIP Services
OTT service providers offering VoIP applications deploy softswitches for efficient call traffic management. A popular example is Skype, one of the most pioneering platforms offering OTT VOIP services, which leverages softswitches to enable global connectivity for calls made over the internet using the Skype app. Another prominent example is WhatsApp, owned by Meta, which uses softswitches to facilitate voice calling to its users.
2. Mobile and Wireless Networks
MNOs, i.e., Mobile Network Operators, utilize softswitches to achieve a variety of goals as mentioned below:
- Softswitches ensure seamless call routing between different carrier networks. Softswitches help in optimizing the flow of calls and data across different networks by selecting the best routes.
- Furthermore, Softswitches also contribute to roaming services by ensuring a seamless transition from the home network to other networks when a mobile phone user travels outside their home area network.
- Another area where softswitches are useful is the signaling and protocol conversion. Softswitches ensure that signals between different carriers and networks are interpreted correctly. They do so by handling the translation of signals from one format to another, called protocol conversion.
3. Emergency Services
In the government and public sector, softswitches are essentially used for emergency communication systems. For critical situations that require law enforcement, fire departments, and medical assistance, softswitches facilitate emergency call routing for swift and rapid response or action.
4. Telecom Service Providers
Though this has been covered already, let’s take a quick look again. Softswitches are an integral part of the working of telecom service providers. While wholesale carriers managing large call traffic leverage Class 4 softswitches, ISPs make use of Class 5 softswitches to manage their local call traffic.
Tips for Choosing the Right Softswitch

Now that you have gained sufficient knowledge about softswitches, it would be a good idea to choose the right softswitch for your needs. I have gathered some essential tips to guide you through the process:
First, Assess your Business Needs
Start with this in mind – your business is unique and has unique requirements. Therefore, when choosing the right softswitch, consider these 5 aspects to identify what your business needs.
- Determine the call volume that you anticipate handling. Identify average and peak call volumes.
- Figure out the specific features your business needs. It can be call routing, billing, IVR, call conferencing, or integration with other tools.
- Whether your existing infrastructure is VoIP, PSTN, or mobile network, it is important to check the compatibility of the softswitch with your network.
- Your communication needs are bound to change, so check how easily the softswitch can scale with your changing needs.
Secondly, Decide Upon the Deployment Model
With the rising popularity of cloud-hosted telecom solutions, many new entrants are curious about where to host their VoIP applications for scalability, reliability, and ease of management.
One Reddit user asked a thoughtful question that captures this sentiment:
What cloud platform is preferred to deploy Telecom or VOIP Application?
Hello! This has been a curious question in my mind for a long time. What cloud platform do you prefer to deploy your VOIP application and why? I know there are multiple applications and platforms, but it would be tremendous help for the newcomer who wants to dive into the VOIP career, so that will help your expert opinion here. Thank you
Source: Reddit
This question reflects a broader concern among professionals entering the VoIP space.
- Network latency in your target region
- Cost efficiency
- Uptime and redundancy
- Support for SIP protocols and firewall/NAT configurations
Here is a pro tip for you: Go with a platform that allows autoscaling, real-time monitoring, and seamless failover.
Thirdly, Evaluate Providers and Products
You need to make a checklist of the following points to shortlist the best providers and solutions.
- Reputation of the vendor
- Features and Functionalities
- Robust Security Measures
- Support Services
- Pricing of the Solution
Fourthly, Conduct Thorough Testing
Almost all the vendors out there offer free trials to interested customers. So why not take advantage of this opportunity, right? This will enable you to test the softswitch in your work environment and check its suitability.
During the trial period, do these 3 things:
- Check the call quality under different conditions
- Use all the features that you wish to use
- Test the integration of the softswitch with existing tools
Fifthly, Make Additional Considerations
Though we have covered most of the key areas to make a good choice, I would like to suggest 3 more aspects that you should consider.
Compliance: Make sure the softswitch solution meets the industry-specific regulations
Future Proofing: Look for a softswitch that can adapt to emerging trends and technologies.
Ease of Use: Don’t forget to consider the interface of the softswitch because ease-of-use matters.
Last, Seek Expert Advice
If you still have questions or doubts, it is best to get in touch with an industry expert. They can provide answers to your complex requirements and guide you through the selection process.
Get Started with REVE – Class 4 and Class 5 Softswitch
REVE Session Border Controller – Class 4 Softswitch

REVE Session Border Controller (SBC) is a powerful and scalable platform for communication service providers. The Class 4 Softswitch Platform has a distributed architecture for network availability & resiliency to prevent any threat. Powered with a real-time billing platform and intelligent routing, REVE SBC makes IP wholesale business more scalable.
- Integrated intelligent firewall for security and reliability
- Distributed architecture & SIP interoperability
- 1+1 hot redundancy
- Scalable
- Real-time billing
iTel Switch – Class 5 Softswitch

iTel Switch is a single Softswitch platform for global Retail, Wholesale, Calling Card, and Call Shop businesses. Being a customizable and scalable VoIP Softswitch with integrated billing, it serves as an ideal platform for all VoIP service providers who want to provide VoIP calling services. Multilevel reseller support, easy end-user interface, integrated billing, intelligent routing, and class 4 & 5 Softswitch features are some of the benefits of iTel Switch.
- Easy rate plan management
- Flexible & advanced routing
- Live call monitoring
- Multilayer security
- Detailed analysis & reporting
- SMS and email-based alert system
- Seamless client management
- Multiple DID management
Conclusion
In the past telecom industry relied heavily on circuit-based switches to establish connections between callers and deliver uninterrupted services. With the advent of software-based technologies, softswitches took over and emerged as a more scalable and flexible alternative to their hardware-based counterparts.
If you, too, are a telecom provider, a communication service provider, or a VoIP service provider, we encourage you to take a free demo of our Class 4 switch and Class 5 switch. Our industry experts are always available to answer any type of queries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of a softswitch in telecom?
A softswitch acts as a central controller for routing and managing VoIP calls. It makes communication systems more scalable, cost-efficient, and easier to maintain by replacing traditional hardware-based switches with software.
Are softswitches the same as PBX systems?
No, a softswitch is typically meant to handle carrier-level traffic, while a PBX system is designed for internal business phone systems. However, a Class 5 softswitch can include PBX-like features such as call forwarding, voicemail, and IVR.
What hardware is needed to deploy a softswitch?
Modern switches are software-based, so their hardware requirements depend on scale. Typically, a reliable server, sufficient RAM storage, redundant power and network connections, and a Session border controller are required if connecting to PSTN. However, with cloud deployment, hardware needs are minimal on the user’s end.
Can a softswitch be hosted on the cloud?
Yes, softswitches are being increasingly hosted on the cloud owing to the various benefits, including eliminating the need for physical infrastructure, offering rapid deployment, lower maintenance, and allowing businesses to scale easily. The trend is increasingly popular among small businesses like startups and service providers offering VoIP services.
What kind of technical expertise is required to manage a softswitch?
Basic technical knowledge might be helpful during the initial setup and configuration of the softswitch. However, today, modern softswitches come with user-friendly dashboards, dedicated onboarding assistance, and managed services. This means non-technical users can also easily operate the softswitch system.

























